
It also opens the possibility of diagnosing T1N using home sleep studies. Our method can reduce time spent in sleep clinics and automates T1N diagnosis. Addition of HLA-DQB1*06:02 typing increased specificity to 99%. A T1N marker based on unusual sleep stage overlaps achieved a specificity of 96% and a sensitivity of 91%, validated in independent datasets. It also reliably scores sleep down to 5 s instead of 30 s scoring epochs. The best model performed better than any individual scorer (87% versus consensus). Accuracy of sleep stage scoring was validated in 70 subjects assessed by six scorers. Here, we used neural networks in approximately 3,000 normal and abnormal sleep recordings to automate sleep stage scoring, producing a hypnodensity graph-a probability distribution conveying more information than classical hypnograms. All rights reserved.Analysis of sleep for the diagnosis of sleep disorders such as Type-1 Narcolepsy (T1N) currently requires visual inspection of polysomnography records by trained scoring technicians.

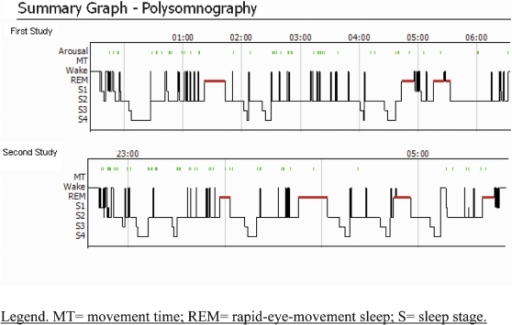
#Ideopathic hupersomnia hypnogram trial
The first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of modafinil have just been published, as well as a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of clarithromycine, a negative allosteric modulator of the γ-aminobutyric acid-A receptor.ĭiagnostic criteria Genetics Homeostatic and circadian regulation Hypersomnolence Idiopathic hypersomnia Immunology Neurochemistry Treatment.Ĭopyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. Until now, the treatment of idiopathic hypersomnia has mirrored that of the sleepiness of narcolepsy type 1 or 2. Differential diagnosis involves a number of diseases and it is not yet clear whether idiopathic hypersomnia and narcolepsy type 2 are not the same condition. Based on neurochemical, genetic and immunological analyses as well as on exploration of the homeostatic and circadian processes of sleep, various pathophysiological hypotheses have been proposed. The condition is disabling, sometimes even more so than narcolepsy type 1 or 2. Idiopathic hypersomnia is most often a chronic condition though spontaneous remission may occur. Yet, MSLT is neither sensitive nor specific and the polysomnographic diagnostic criteria require continuous readjustment and biologic markers are still lacking. Polysomnography (PSG) followed by a multiple sleep latency test (MSLT) is mandatory, as well as a 24 h PSG or a 2-wk actigraphy in association with a sleep log to ensure a total 24-h sleep time longer than or equal to 66O minutes, when the mean sleep latency on the MSLT is longer than 8 min. It is often accompanied by sleep of long duration and debilitating sleep inertia. The key manifestation is hypersomnolence. A familial background is often present but rigorous studies are still lacking. Disease onset occurs most often during adolescence or young adulthood. No epidemiological studies have been conducted so far. The diagnostic criteria of idiopathic hypersomnia have varied with the successive revisions of the International classifications of sleep disorders, including the recent 3rd edition. Idiopathic hypersomnia continues to evolve from the concept of "sleep drunkenness" introduced by Bedrich Roth in Prague in 1956 and the description of idiopathic hypersomnia with two forms, polysymptomatic and monosymptomatic, by the same Bedrich Roth in 1976.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
